The repo rate in India
Earlier this month, RBI raised the repo rate by 40 basis points to 4.40%, with immediate effect
What is the Repo Rate?
- It is one of several direct and indirect instruments used by RBI for implementing monetary policy.
- It is fixed interest rate at which RBI provides overnight liquidity to banks against the collateral of government and other approved securities under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF).
- When banks have short-term requirements for funds, they can place government securities that they hold with central bank and borrow money against these securities at the repo rate.
- It serves as key benchmark for lenders to in turn price the loans they offer to their borrowers.
Why is the repo rate such a crucial monetary tool?
- When government, central banks repurchase securities from commercial lenders, they do so at a discounted rate that is known as repo rate.
- Repo rate system allows central banks to control money supply within economies by increasing or decreasing the availability of funds.
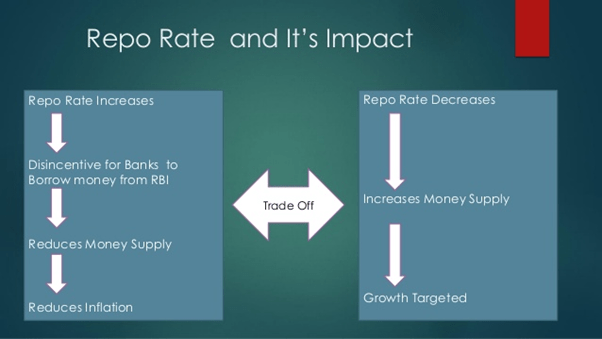
How does the repo rate work?
- It functions as monetary tool to regulate availability of liquidity or funds in the banking system.
- When repo rate is decreased: banks may find an incentive to sell securities back to the government in return for cash.
- This increases money supply available to general economy.
- When the repo rate is increased: lenders would think twice before borrowing from the central bank at the repo window.
- It reduces availability of money supply in the economy.
- Since inflation is caused by more money chasing the same quantity of goods and services available in an economy, central banks tend to target regulation of money supply as a means to slow inflation.
Impact of repo rate change on inflation
- Inflation can broadly be: mainly demand driven or result of supply side factors.
- Supply side factors push costs of inputs used by producers of goods and providers of services.
- It spur inflation, or most often caused by a combination of both demand and supply side pressures.
- Changes to the repo rate to influence interest rates and the availability of money supply majorly work only on demand side.
- It makes credit more expensive and savings more attractive and therefore dissuading consumption.
Exam track
Prelims take away
- Open Market Operations
- Repo rate
- Reverse repo rate
- Liquidity Adjustment Facility