Lumpy skin disease led to stagnation in milk production: Centre
- The Centre has said that the “stagnation” in milk production and the following scarcity of ghee and butter is possibly due to the impact of the lumpy skin disease (LSD) that led to the death of close to 1.89 lakh cattle in recent times.
Lumpy skin disease (LSD)
- LSD is a viral disease caused by the Capripox virus of the Poxviridae family which is also called the Neethling virus.
- LSD causes prolonged morbidity in bovines such as cattle and buffaloes.
- LSD was first reported in Africa (Zambia) in 1929 and has now emerged as a transboundary animal disease as it has spread to Asia and Europe.
- According to the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), LSD has a mortality rate of 1 to 5%.
Symptoms of LSD
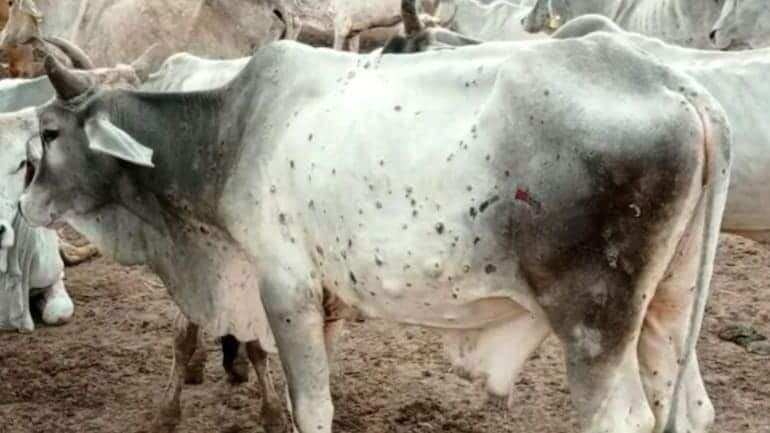
- LSD causes fever and nodules all over the body, especially around the head, neck, limbs, udder and genitals.
- The animals infected with the LSD virus usually lose weight suddenly.
- Other symptoms like fever and lesions in the mouth, along with a reduced milk yield.
- Excessive nasal, salivary secretion and miscarriage are also associated with LSD.
Transmission of LSD
- LSD spreads through blood-feeding insects like flies, mosquitoes and ticks.
- LSD is not a zoonotic disease which means that it does not spread from animals to humans and hence Lumpy skin disease does not affect humans.

Treatment for LSD
- LSD is curable and recovery will be fast if treatment is given at the early stages of the infection.
- There are three licensed vaccines for LSD which include the lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV) Neethling vaccine, Kenyan sheep and goat pox (KSGP) O-180 strain vaccines and Gorgan goat pox (GTP) vaccine.
- Vaccination against LSD is covered under the Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme of India.
Prelims Take Away
- Limpy Skin Doisease
- Zoonatic Diseases
- World Organisation for Animal Health