5G to improve the Infrastructure and enable new applications.
- With increased capacity, lower latency, and energy efficiency, 5G is expected to significantly improve the state of art and enable new applications.
- To reduce cost, the Department of Telecom (DoT) may use infrastructure owned by the power sector distributors for deployment of 5G small cells (small 5G towers).
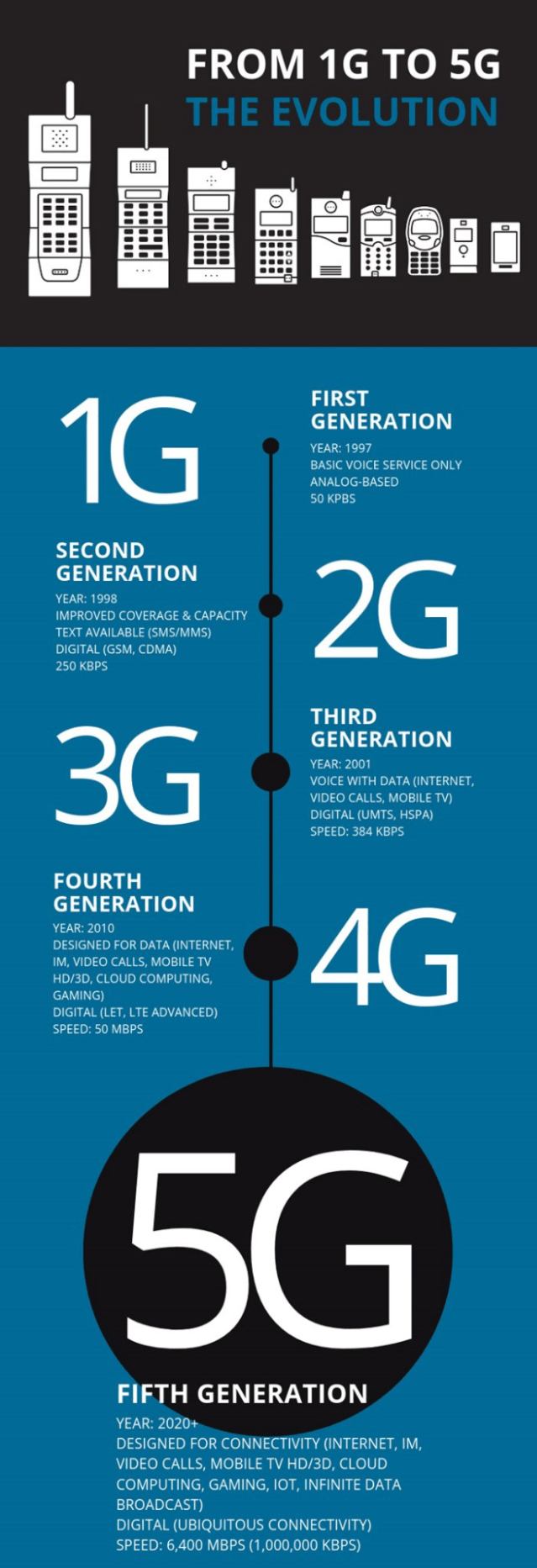
About 5G
- 5G represents the allocation of new spectrum to increase capacity.
- Since most of the spectrum at lower frequencies is already being utilised — much of this new spectrum is being allocated at higher frequencies.
- 5G infrastructure is being built from ground up, there is a chance to redesign the technology
- To make it more suitable for the evolving communication needs of the future, like 6G.
Volume and Bandwidth of data for 5G
- Over the next several years the volume of data is expected to exponentially increase
- 5G places a lot of importance on energy efficiency to avoid exponential rise in energy consumption..
- Radio electronics refers to a broad range of technologies that can transmit, receive and process wireless signals.
- While these technologies can utilize electromagnetic spectrum that goes all the way up to 300GHz, the lower frequencies of this spectrum are particularly attractive.
- Lower frequency signals can travel longer distances and penetrate obstacles with lesser attenuation.
- Electronic components (amplifiers, transmitters, receivers) operating at lower frequencies are also easier to design and manufacture.
- The bandwidth in the lower frequencies has already been allocated for several applications (mobile communications currently use the spectrum from 800MHz to 2.5 GHz).
New spectrum for 3GHz
- With the increasing demand for mobile services, the currently allocated spectrum is proving inadequate.
- At the simplest level, 5G represents the allocation of new spectrum to increase capacity.
- This new spectrum is being allocated at higher frequencies.
- The first deployments in India will be around 3GHz, but will expand to 25 GHz and beyond.
- As 5G services evolve to occupy higher frequencies, it will significantly increase the bandwidth available for mobile services.
- The design of the transmitting and receiving higher frequency equipment becomes more complex. Signal attenuation also increases.
- The coverage area of each cell tower will decrease which will require the towers to be more closely spaced.
- At higher frequencies it becomes easier to direct a signal in a specific direction. So, signals transmitted from a cell tower can be more precisely directed at a specific user and provide higher capacity.
- Rather than spreading out in various directions which is just a waste of energy.
Evolving communication needs
- Since much of the 5G infrastructure is being built from ground up
- There is a chance to redesign the technology to make it more suitable for the evolving communication needs of the future.
- 5G places special emphasis on low latency, energy efficiency and standardization.
- Today, the components that make up wireless telecom interact with each other using proprietary protocols that are vendor specific.
- To enable the rapid deployment of 5G infrastructure there is an industry-wide effort to standardize interaction between components.
- Greater standardization would enable service providers to build their infrastructure, ‘mixing and matching’ components from multiple vendors.
- Switching vendors would also be easier which would foster competition and lower costs.
- Existing wireless communication infrastructure is primarily designed around the needs of mobile phones.
- Several emerging applications in factory automation, gaming and remote healthcare have more stringent latency requirements.
- Self-driving cars are an illustrative example.
- Low delays between transmission and reception of messages are extremely critical when these cars have to cooperate with each other to avoid accidents.
Advanced R&D
- There is a lot of research in both industry and academia centered around 5G.
- An interesting topic is the convergence of positioning, sensing and communication.
- Traditionally, positioning, sensing and communication have been seen as separate technologies (for e.g GPS is used for positioning, and radar for sensing).
- All three technologies involve transmission and reception of radio signals
- Possibility for positioning and sensing to piggyback on 5G infrastructure that is primarily meant for communication.
- The key features of 5G (such as increased bandwidth availability and antenna directionality)
- Will improve the accuracy of positioning and sensing.
- There is also a lot of research around cost and energy efficient electronic devices that can transmit and receive high frequency signals.
- Engineers are already busy prototyping a 6G system which would utilize the large amounts of available spectrum at frequencies above 100 GHz.
Prelims take away
- 5G technology
- Latency
- Spectrum for 4G, 5G and 6G